DC-to-DC converters play a vital role in modern electronic systems, allowing devices to function efficiently by converting one level of DC voltage into another. As electronic devices such as ICs and MOSFETs operate at various voltage levels, the need for converters to adjust these levels becomes essential. Two key types of converters, the Buck Converter and the Boost Converter, are commonly used for these adjustments. The Buck Converter lowers the input voltage to a desired lower output, while the Boost Converter increases it to a higher level.
In addition to altering voltage levels, DC-to-DC converters also improve circuit efficiency, manage ripple effects, and influence load-transient response. The selection of external components, including capacitors, inductors, and diodes, greatly depends on the operational requirements of a system, such as its input and output specifications. Designing these circuits involves a combination of precision, expertise, and experience to ensure that all components work in harmony for optimal performance.
Applications and Importance of DC-to-DC Converters
DC-to-DC converters are integral in applications where battery voltage fluctuates. Whether a battery's voltage is higher or lower than the device's required operating voltage, converters ensure a constant voltage supply to the load. This feature is essential for many portable electronic devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and even electric vehicles, which require consistent voltage regardless of battery levels.
For instance, in electric vehicles, the battery voltage can vary significantly depending on its state of charge. A DC-to-DC converter ensures that critical systems receive a stable voltage, whether stepping it up or down as needed. This technology ensures that devices continue to function efficiently while maximizing battery life.
Working Principle of DC-to-DC Converters
The principle behind DC-to-DC converters is fairly straightforward. In essence, these converters store energy temporarily and then release it to provide a regulated output. An inductor, an essential component in the converter, plays a crucial role in storing energy as magnetic energy during the 'on' phase when the switch is closed. When the switch is 'off,' the stored energy is released to the output.
A capacitor, located on the output side, ensures that the voltage remains steady by filtering any fluctuations in the current. This design ensures that the output voltage remains constant, allowing the converter to provide consistent voltage to the load even during transient conditions.
Types of DC-to-DC Converters
DC-to-DC converters come in various types, each suited to different applications and operating environments. These include:
1. Magnetic Converters
Magnetic DC-to-DC converters periodically store and release energy using magnetic fields within inductors or transformers. Their operating frequency can range from 300 kHz to 10 MHz. By adjusting the duty cycle, the converter can regulate the amount of energy transferred to the load, making it easier to control the power supply. Transformers in these converters also provide isolation between the input and output, which is essential for many high-voltage applications.
2. Non-Isolated Converters
Non-isolated converters are more straightforward and are used when the voltage change between input and output is small. These converters have a common ground between input and output, which simplifies design but limits protection against high-voltage spikes or electrical noise. Non-isolated converters are often used in lower-power applications where isolation is not a priority.
3. Step-down/Buck Converters
Buck converters are among the most widely used DC-to-DC converters. They reduce the input voltage to a lower output voltage based on the switching duty cycle. This type of converter is ideal for applications where the input voltage is higher than the required output, such as in battery-powered devices that need a lower operating voltage.
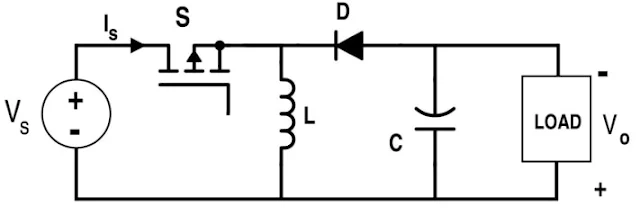
4. Step-up/Boost Converters
Boost converters perform the opposite function of buck converters, increasing the input voltage to a higher output. These converters use similar components but are arranged to step up the voltage. Boost converters are ideal in situations where a low input voltage needs to be increased, such as in solar-powered systems where the input voltage can be quite low.
5. Buck-Boost Converters
A buck-boost converter can either increase or decrease the input voltage based on the duty cycle of the switch. This versatility makes buck-boost converters useful in applications where the input voltage can fluctuate above or below the required output. One notable feature of this type of converter is that the output voltage is inverted relative to the input voltage, giving it the alternative name of "voltage inverter."
6. Isolated Converters
Isolated converters provide electrical isolation between the input and output. This isolation is crucial in high-voltage applications, such as industrial power supplies, where safety and noise reduction are top priorities. The isolation ensures that any high-voltage spikes or interference on the input side do not affect the output.
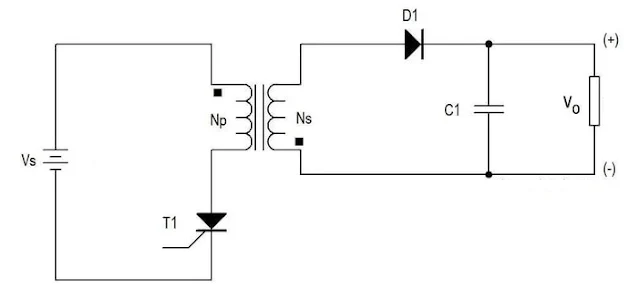
I. Flyback Converters
Flyback converters operate similarly to buck-boost converters but use a transformer instead of an inductor. The transformer not only provides energy storage but also isolates the input and output. Flyback converters are widely used in power supplies for consumer electronics due to their simplicity and effectiveness in low to medium-power applications.
II. Forward Converters
Forward converters also use a transformer but operate differently from flyback converters. Instead of storing energy, they transfer it directly between the input and output, offering greater efficiency. Forward converters are preferred in applications where higher power and efficiency are required.
Advantages of DC-to-DC Converters
DC-to-DC converters provide several advantages in power management systems:
- Power Efficiency: They enhance power supply efficiency by delivering only the required voltage, reducing energy waste.
- Voltage Isolation: Certain types, such as isolated converters, provide crucial isolation between the input and output, improving safety in high-voltage applications.
- Space Saving: By adjusting voltage levels within a system, they help reduce the size and complexity of the overall design, especially in battery-powered devices.
- Integrated Circuit Design: Many modern converters are available as integrated circuits, simplifying circuit design and reducing the number of external components required.
- Battery Life Extension: By efficiently managing voltage, converters can extend the operational life of batteries, which is essential in portable electronic devices.
Disadvantages of DC-to-DC Converters
Despite their advantages, DC-to-DC converters also have some drawbacks:
- Switching Noise: High-frequency switching in converters can introduce electrical noise into the system, which may interfere with sensitive components.
- Cost: The need for additional external components, such as inductors, capacitors, and heat sinks, can increase the overall cost of the converter.
- Ripple and Losses: Converters are prone to ripple effects in the output, which may require additional filtering to stabilize. They can also suffer from power losses, especially when operated at extreme input or output voltage levels.
Conclusion
DC-to-DC converters are essential components in modern electronic systems, allowing for efficient voltage regulation across various applications. From step-up and step-down converters to isolated and non-isolated designs, these converters offer versatility and adaptability for powering devices with different voltage requirements. While they come with certain challenges, such as switching noise and ripple, their advantages in efficiency, space saving, and battery management make them indispensable in electronics.